The metropolitan region of Delhi presently has a population of 32 million people, an increase of 2.84 percent from the previous year. The Indian government has been executing numerous projects to decongest Delhi and provide improved transportation to residents of the Delhi-NCR region. One such initiative is the construction of India's first regional rapid transit system, which will be built at a cost of 30,274 crores and is currently underway. The Regional Rapid Transit System (RRTS) project is being implemented by the National Capital Region Transport Corporation (NCRTC), a joint venture firm formed by the government of India and the states of Delhi, Haryana, Rajasthan, and Uttar Pradesh.
With a design speed of 1800km/h, this first regional rapid transit system will connect Delhi and its three neighboring states: Rajasthan, Haryana, and Uttar Pradesh, enabling seamless travel by significantly reducing commuters' travel time to less than an hour. The investment project is envisaged to be beneficial for the development of the region and to help connect townships and centers of economic activity that are planned along the corridor.
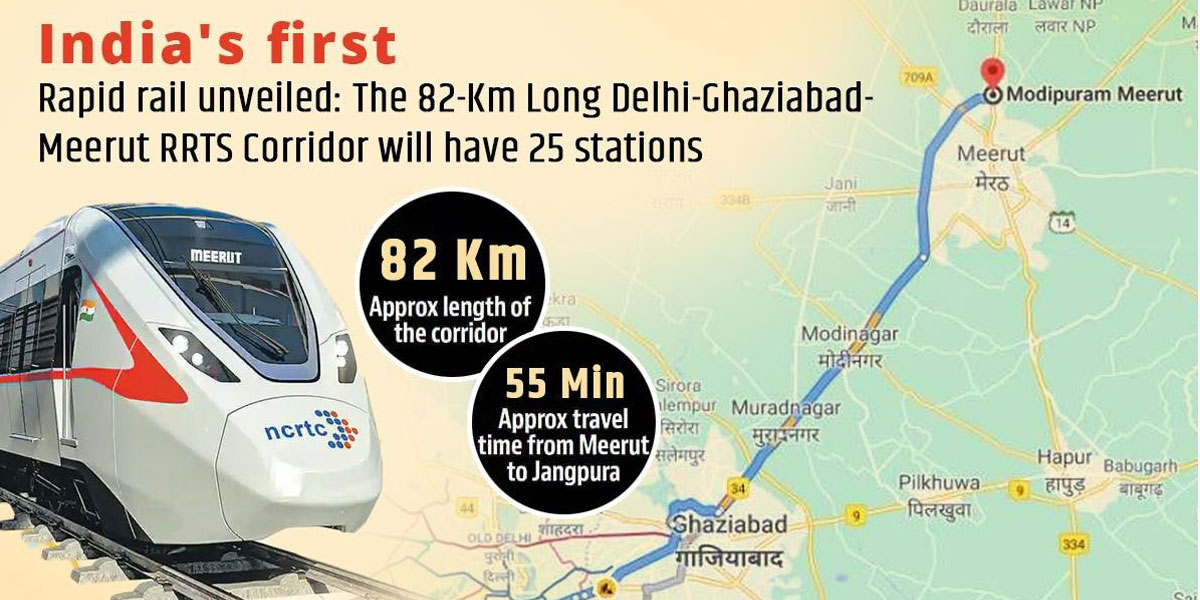
The proposed alignment passes through the dense developments of Delhi, Ghaziabad, and Meerut. It will comprise a double-line, standard gauge; a rapid railway system built on elevated viaducts and going underground in heavily populated areas. About 70% of the civil construction work has been completed on the priority section of the corridor. It will connect Modipuram in Meerut to Sarai Kale Khan in Delhi. The viaduct will be built along the central median strip of the highway connecting Delhi to Meerut. The entire route length of the corridor is about 82 kilometers (km). As many as 30 RRTS train sets, each consisting of six coaches will be made operational for the regional services, while 10 RRTS train sets, each having three coaches, will be made functional for the city services in Meerut.
The Delhi-Meerut RRTS project will be connected to most modes of transport at important stations. These modes include the Delhi Metro, bus terminals, and stations.
Currently, National Highway 24 connects Delhi with Meerut, and it is the main and most-used road link between the two cities, carrying the majority of traffic between Delhi and Meerut, Hardwar, and Dehradun. As a result, the RRTS will have multimodal integration with inter-state bus terminals, bus stands, railway stations, and metro stations to make it easier for people to switch from one mode of public transportation to another.
The Delhi-Meerut RRTS corridor will have 22 stations, out of which 16 stations will be regional stations while 6 stations will be located in Meerut. The Delhi-Meerut The RRTS line will include 22 stations, 16 of which will be regional stations and 6 of which will be located in Meerut. The 17-kilometer Sahubabd-Duhai segment, which is the priority phase of the Delhi-Meerut RRTS, is expected to be operational by 2023 and will arrive at Ghaziabad's Duhai depot soon. The tracks have been laid out and preparations are in full swing for the test of the train at the depot. An administrative building has also been constructed in the depot for the operation of the RRTS trains.
These semi-high-speed aerodynamic trains are energy-efficient, and designed to offer top-notch comfort and safety features for a premium passenger experience for commuters, including those especially able. The estimated daily ridership is expected to be around 8lakhs. Designed at Alstom’s Hyderabad engineering center and manufactured at Savli (Gujarat), these trains are 100% indigenous, in line with the government’s Make-in-India and Aatmanirbhar Bharat ambitions. Some of the features of this state-of-the-art Made in India coach include: ergonomically built 2×2 transverse seating, wide gangway for comfortable standing space, overhead luggage racks, CCTV cameras, fire & smoke detectors, intercom, fire extinguisher, exterior camera, door status indicators, grab handles, Wi-Fi, laptop/mobile/USB charging stations, dynamic route display maps, auto controlled ambient lighting system, large windows for a panoramic view, and ergonomically designed areas to support the specially-abled & medical emergencies.
The Delhi-Meerut RRTS is designed to relieve traffic congestion and reduce fuel consumption in the region. Other advantages of the corridor include reduced travel costs and time, enhanced safety, lower emissions, more economic activity, and so on. By 2025, the entire route, which includes 22 stations, is expected to be open to the public.
This project holds special significance as it will be a major push for the "Make in India" program. This upcoming transformational project will help to improve the quality of life for those living in nearby regions. RRTS will lead to a significant boom in the real estate sector, which will have an impact on the price of housing as well as the commercial sector. The development of this transport system has led to an increase of 65.8% in prices within the Meerut region, indicating a better way for the infrastructure industry along with the world-class transportation facility.