
NITI Aayog seeks consultant to evaluate the operation of NHAI
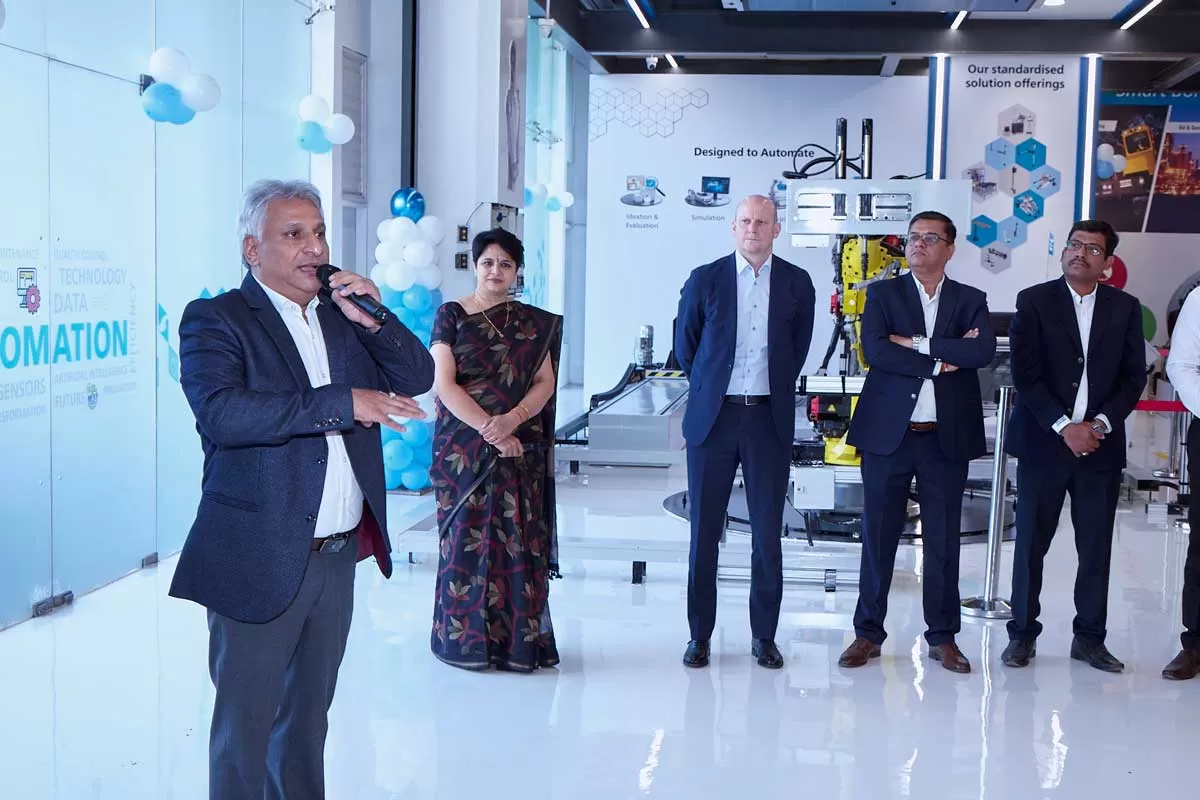

Atlas Copco Unveils Innovation Centre in Pune for Smart Manufacturing
Atlas Copco Tools has inaugurated its first Smart Factory Innovation Centre in India, a cutting-edge facility in Pune designed to showcase advanced technologies powering Smart Integrated Assembly ecosystems. The centre will serve as a hub for businesses across automotive, aerospace, electronics, heavy machinery, and manufacturing sectors to explore automation and smart manufacturing solutions for zero-defect production.The Innovation Centre offers hands-on demonstrations of the latest torquing and dispensing technologies, highlighting software-driven solutions that optimize efficiency, enhance..
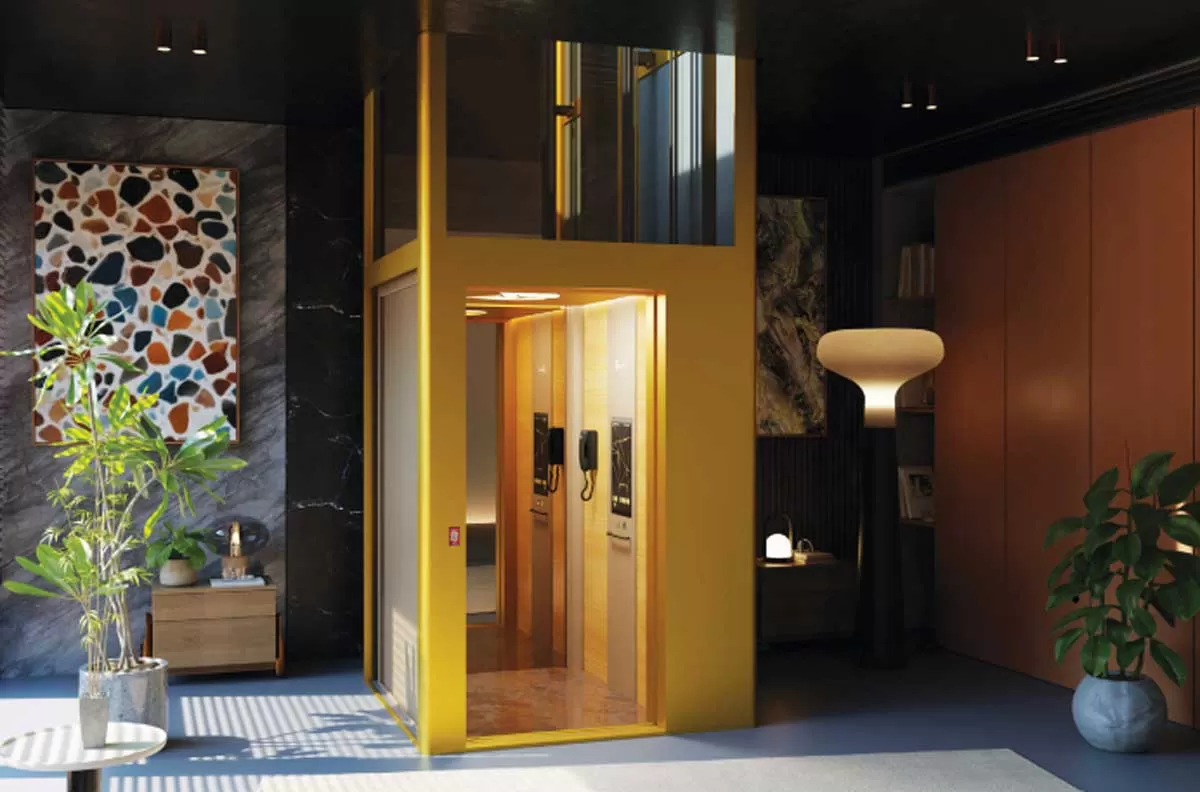

Elite Elevators Unveils India’s First Fully Customizable Home Elevator
Elite Elevators, a leader in the premium home lift segment, has launched Elite Elevators Bespoke—India’s first fully customizable luxury home elevator. The launch event, held at the company’s Chennai headquarters, showcased how the new offering redefines residential mobility by integrating state-of-the-art technology with personalized design.Speaking on the launch, Vimal Babu, Founder and CEO, Elite Elevators, said, “At Elite Elevators, our mission has always been to revolutionize home mobility with world-class innovations. Through its enhanced customizable features, our Bespoke elevat..
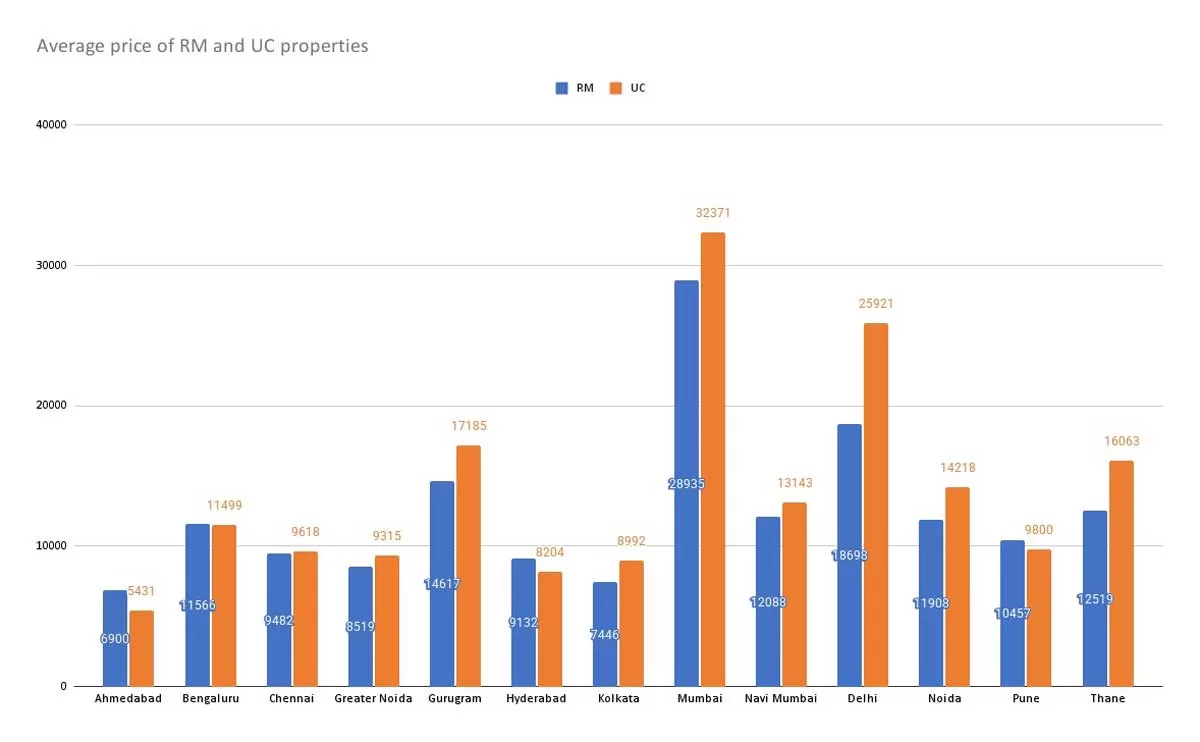
Under-Construction Homes Now Costlier Than Ready-to-Move Properties
Under-construction (UC) homes are now more expensive than ready-to-move (RTM) properties across major Indian metros, according to the latest insights from Magicbricks.In Delhi, UC homes are priced at Rs 25,921 per sq. ft., surpassing RTM properties at Rs 18,698 per sq. ft. Similarly, in Gurugram, UC homes cost Rs 17,185 per sq. ft., compared to Rs 14,617 per sq. ft. for RTM properties.Mumbai, India’s costliest real estate market, has also seen a sharp rise, with UC home prices soaring 33.4 per cent Y-o-Y in Q1 2025 to Rs 32,371 per sq. ft., while RTM properties stand at Rs 28,935 per sq. ft...














