Rural India is experiencing a significant transformation through the digitisation of land records, which modernises land ownership management. This initiative enhances transparency and efficiency in land administration, benefiting millions of rural households. Union Minister of Rural Development, Shri Shivraj Singh Chouhan, recently highlighted the importance of this transition, addressing longstanding challenges related to complex paperwork and ownership disputes. Since 2016, nearly 95% of land records in rural India have been digitised, representing a crucial step toward ensuring secure and accessible land ownership.
The digitisation of land records in India has revolutionised land management by tackling traditional challenges such as disputes, fraud, and inefficient manual processes. Ownership information is now easily accessible online, promoting transparency and reducing illegal encroachments. Digitised records simplify dispute resolution, alleviating court burdens, and empower marginalised communities by improving access to land rights. The integration with geospatial mapping enhances land management, enabling accurate surveys and planning. In situations involving land acquisitions or disasters, digital records ensure fair and timely compensation. Overall, this shift has facilitated a more transparent, accessible, and efficient land governance system in India.
The Digital India Land Records Modernisation Programme (DILRMP), formerly known as the National Land Record Modernisation Programme, was restructured as a Central Sector Scheme in April 2016, with full funding from the central government. Its primary objective is to create a modern and transparent land records management system through the development of an Integrated Land Information Management System. This system aims to provide real-time land information, optimise land use, benefit landowners and potential buyers, support policymaking, reduce land disputes, prevent fraudulent transactions, eliminate the need for physical office visits, and facilitate data sharing among various organisations.
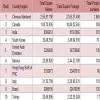
Significant progress has been made under DILRMP, with around 95% of land records computerised, covering over 626,000 villages. Digitisation of cadastral maps has reached 68.02% at the national level. Additionally, 87% of Sub-Registrar Offices (SROs) have been integrated with land records. The government has extended DILRMP until 2025-26, introducing new features such as Aadhaar-based integration with land records and the computerisation of revenue courts.
Key initiatives under DILRMP
- Unique Land Parcel Identification Number (ULPIN): This 14-digit alphanumeric code is assigned to each land parcel based on its geo-coordinates. Implemented in 29 States and Union Territories (UTs), it streamlines real estate transactions, resolves property disputes, and enhances disaster management efforts.
- National Generic Document Registration System (NGDRS): This e-registration system provides a uniform process for document registration across the country, enabling online entry, payments, appointments, and document searches. So far, 18 States and UTs have adopted it, with 12 others sharing data with the national portal.
- e-Court Integration: Linking land records with e-Courts aims to provide authentic land information to the judiciary, facilitating faster case resolution and reducing land disputes. Integration has been implemented in 26 States and UTs.
- Transliteration of Land Records: To overcome language barriers in accessing land records, this program transliterates land documents into any of the 22 languages listed in Schedule VIII of the Indian Constitution. It is currently operational in 17 States and UTs.
- Bhoomi Samman: This initiative recognises 168 districts across 16 States for achieving "Platinum Grading" by completing over 99% of the program’s core components, including land record computerisation and map digitisation.
The Government of India is leading a transformative change in land governance, focusing on enhancing the transparency and accessibility of land information. By leveraging modern technologies like geospatial mapping and unique land parcel identification, this initiative aims to create a more organised and efficient approach to managing land records. This change is particularly crucial for marginalised communities, empowering them with secure and accessible proof of ownership, which is essential for economic growth and stability. As land records become clearer and more accessible, they pave the way for a more inclusive and equitable society, where every individual can claim their rightful place and contribute to the nation’s progress.
(PIB Delhi)