Solar Innovation: Laser-Doping Technique Elevates Cell Performance
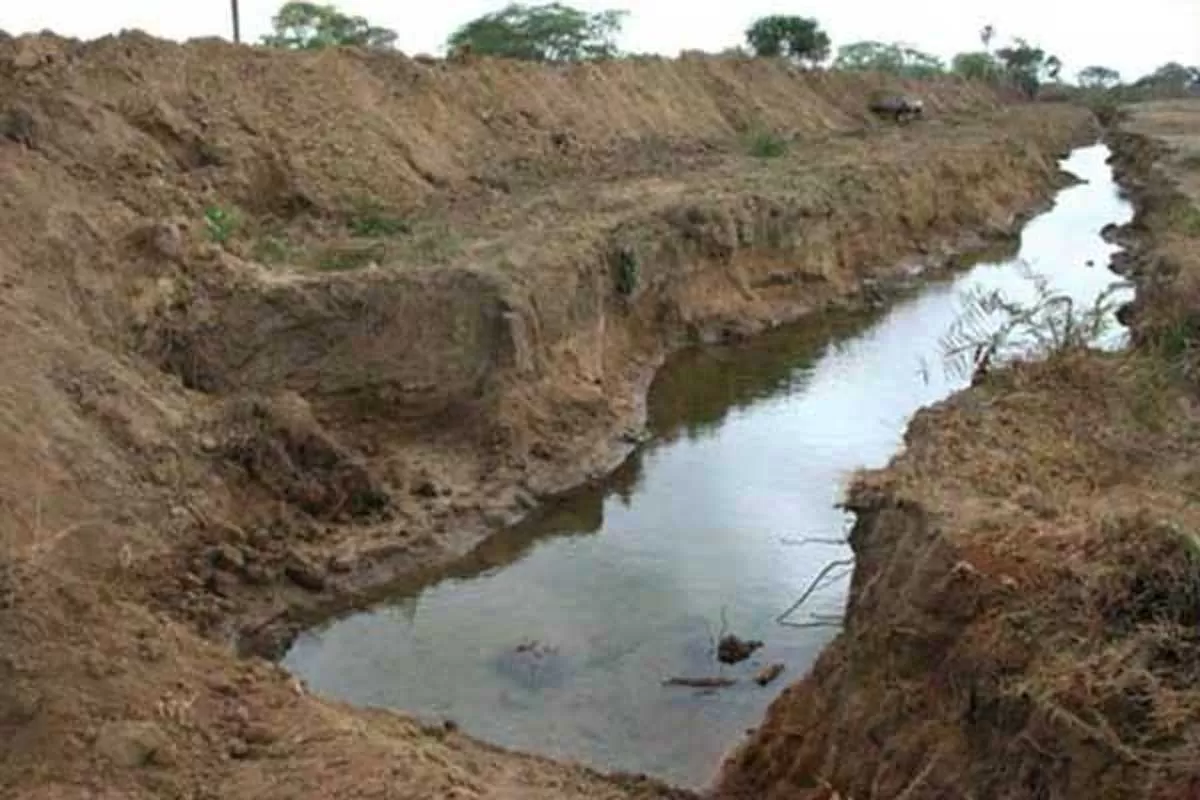

Canal Water Boost for Mudki
In a significant push for public health and urban development, MLA Rajneesh Dahiya has announced a Rs.280 million canal water supply project for Mudki town in the Ferozepur Rural constituency. The initiative aims to provide clean drinking water to every household within Mudki’s municipal limits. Speaking about the development, Dahiya said the project falls under the Centre’s AMRUT (Atal Mission for Rejuvenation and Urban Transformation) scheme and is being carried out with the support of Punjab Chief Minister Bhagwant Singh Mann and Local Government Minister Dr. Inderbir Nijjar. “This ..
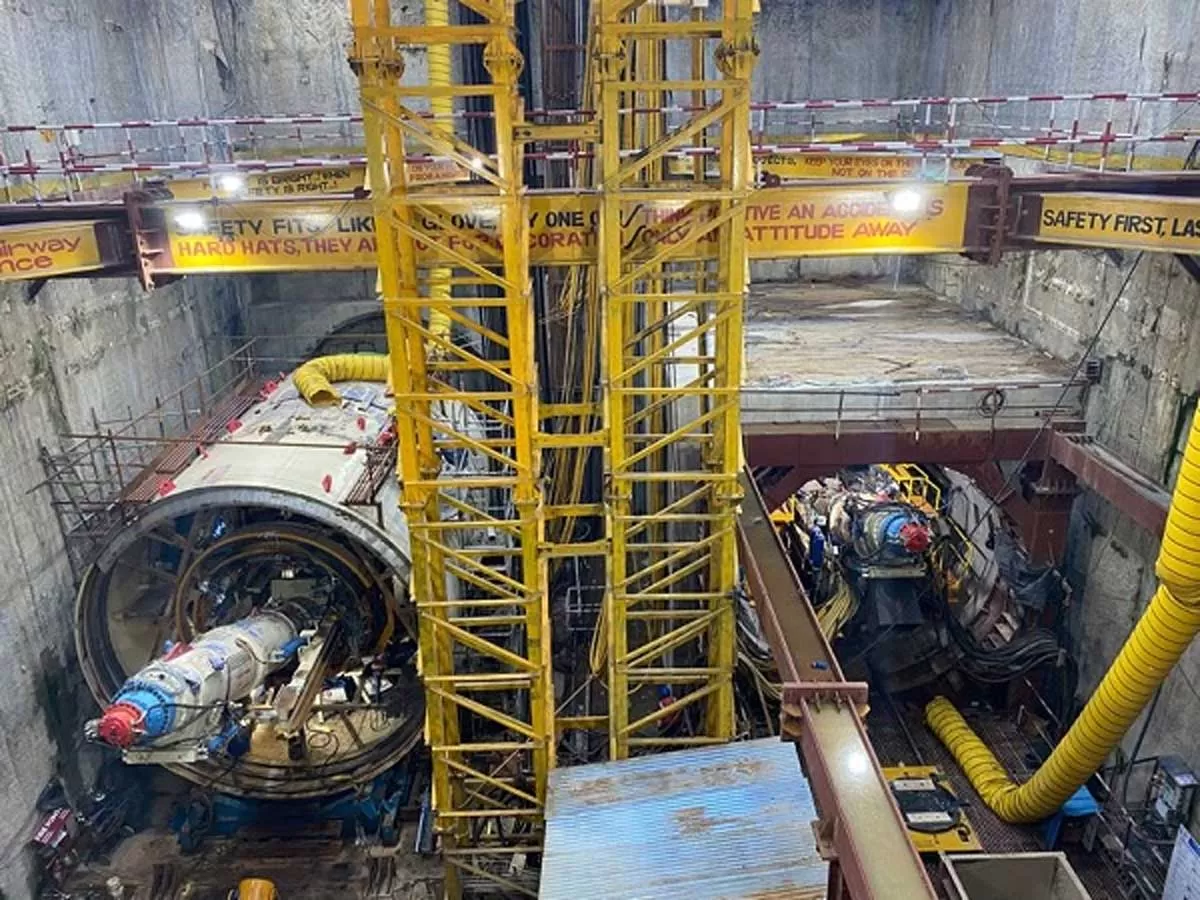

6 Tunnel Boring Machines Idle in Chennai
Six tunnel boring machines (TBMs) deployed by the Chennai Metro Rail Limited (CMRL) are currently lying idle beneath city roads, stuck in limbo due to delayed construction of underground stations at Moolakadai, Perambur, and Mandaveli. The TBMs, launched as part of Corridor 3 of the Phase II Metro project from Madhavaram to SIPCOT, have reached their designated stations but are unable to proceed as the station boxes are incomplete. Without a completed diaphragm wall or station box, the machines cannot break through or be dismantled for reuse. According to CMRL officials, the root of the dela..
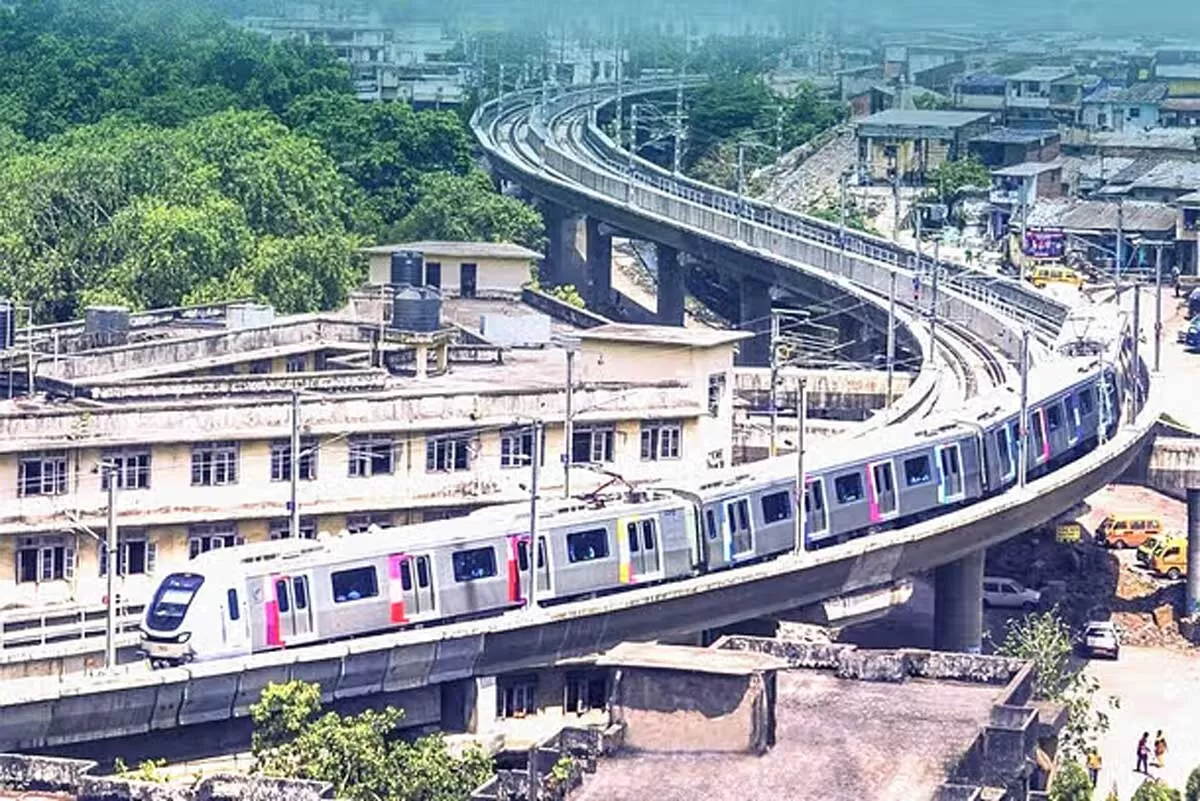

Mumbai Metro 3 Nears Launch
The Mumbai Metro Rail Corporation shared a sneak peek of the newly completed Acharya Atre Chowk station on Metro Line 3 (Aqua Line) this Sunday, drawing both praise and impatience from the public. Located on the 9.77 km stretch between Bandra Kurla Complex (BKC) and Worli, the underground station is part of a long-anticipated corridor that promises to ease traffic and boost east-west connectivity. The social media update, posted by the handle @MumbaiMetro3, featured images of the station’s sleek new interiors. But the post quickly sparked a flurry of comments, with several users demanding c..














