Australia could achieve net-zero emission by 2050

Samridh, CEID Launch High-Capacity Biogas Plant in Moradabad
Samridh Bioenergy has broken ground on a 12 TPD compressed biogas (CBG) plant in Moradabad, Uttar Pradesh, under the MNRE’s National Bioenergy Programme. Spread across 12 acres, the plant will process 270 tonne of organic waste daily and generate 30,000 cubic metre of biogas per day.CEID Consultants and Engineering Pvt Ltd has been appointed as the EPC contractor, responsible for the complete design, procurement, and construction of the plant. Equipped with four multi-feed digesters, the facility will accept a mix of press mud, cow dung, chicken litter, and vegetable waste, supporting contin..
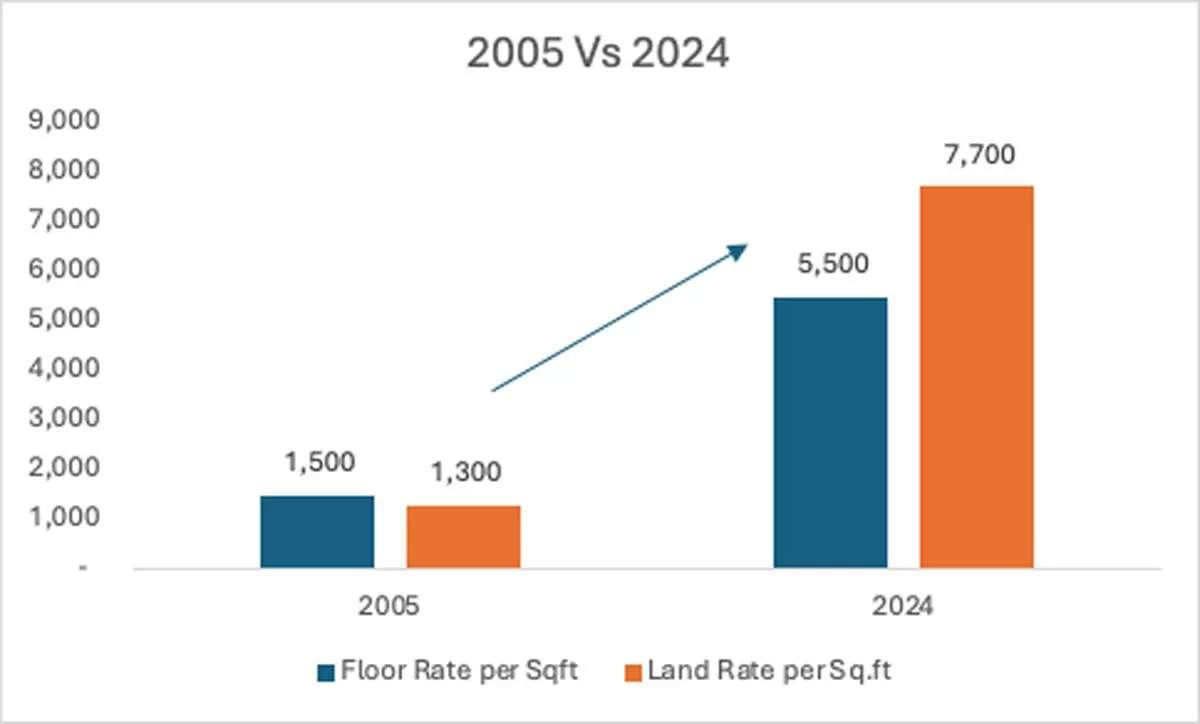
Delhi Micro-Markets Drive Up Housing Prices: Grihum Study
A new study by Grihum Housing Finance reveals that the rise of micro-markets across Delhi-NCR is fuelling real estate price appreciation, especially in the affordable housing segment. Key drivers include renewed post-pandemic interest, migration trends, and government schemes like PMAY.According to the study, over the past two decades, floor rates have risen 267 per cent, from Rs 1,500 per sq ft in 2005 to Rs 5,500 in 2024. In the same period, land rates surged 492 per cent, from Rs 1,300 to Rs 7,700 per sq ft. The sharp increase highlights strong capital appreciation in Delhi’s emerging loc..

Covestro Develops PCR Polycarbonates from End-of-Life Headlamps
Materials manufacturer Covestro has launched post-consumer recycled (PCR) polycarbonates made from end-of-life automotive headlamps, in a move aimed at strengthening circularity in the auto industry. These TÜV Rheinland-certified grades, containing 50 per cent recycled content, are now commercially available for new automotive applications.Developed under a joint programme led by GIZ, with Volkswagen and NIO as key partners, the recycled material is currently being validated for use in future vehicle models.""This new line of polycarbonate represents a significant step in supporting the autom..