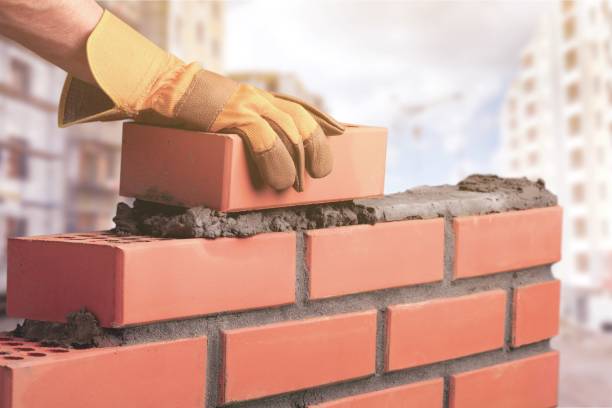
Researchers create tech to develop energy efficient walling materials
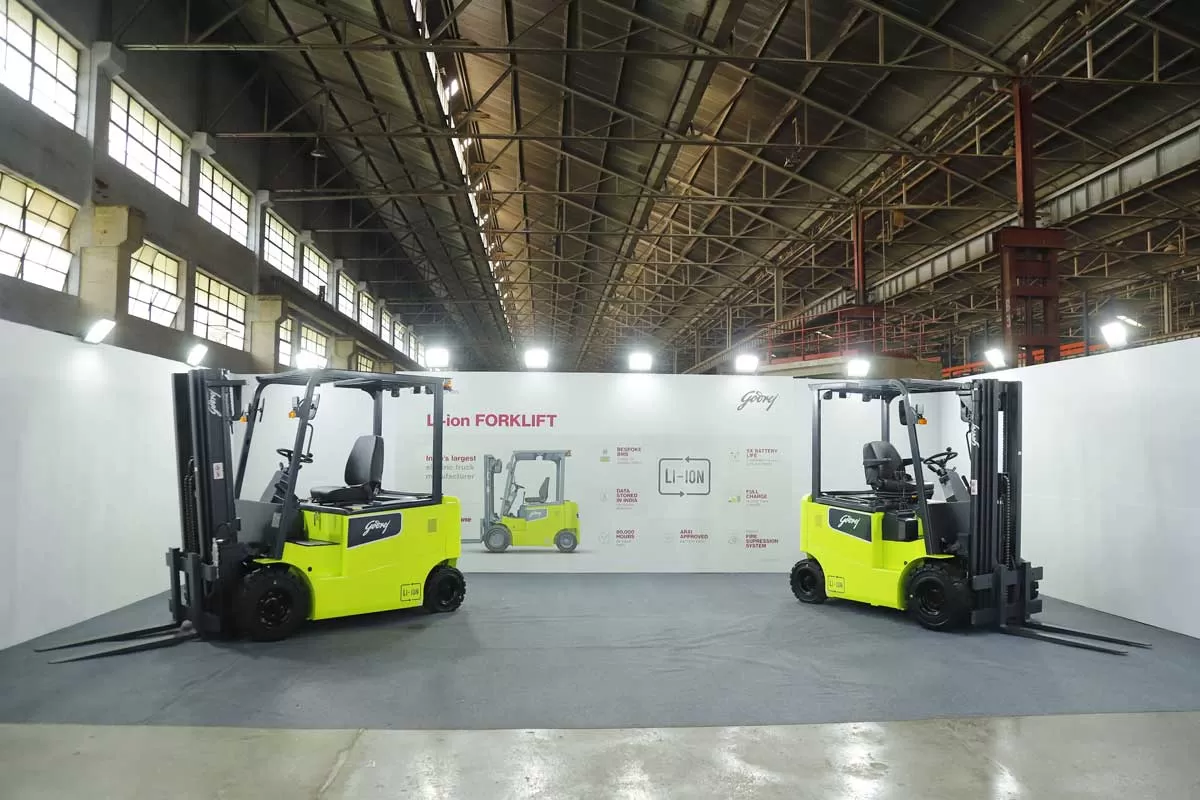


Godrej Material Handling Leads East India with 21% Market Share
The Material Handling business of Godrej & Boyce, a part of Godrej Enterprises Group, is powering industrial growth in Eastern India marking over 60 per cent Y-o-Y growth in the Jamshedpur region for FY25. Solidifying its market leadership, the business commands a dominant 21 per cent market share in the Eastern region, serving as a crucial enabler for the region’s manufacturing sector. At the Indomach Expo in Jamshedpur, the business is showcasing its next-generation forklift to meet evolving needs of Eastern India’s industrial corridor. Jamshedpur, Eastern India’s industrial po..
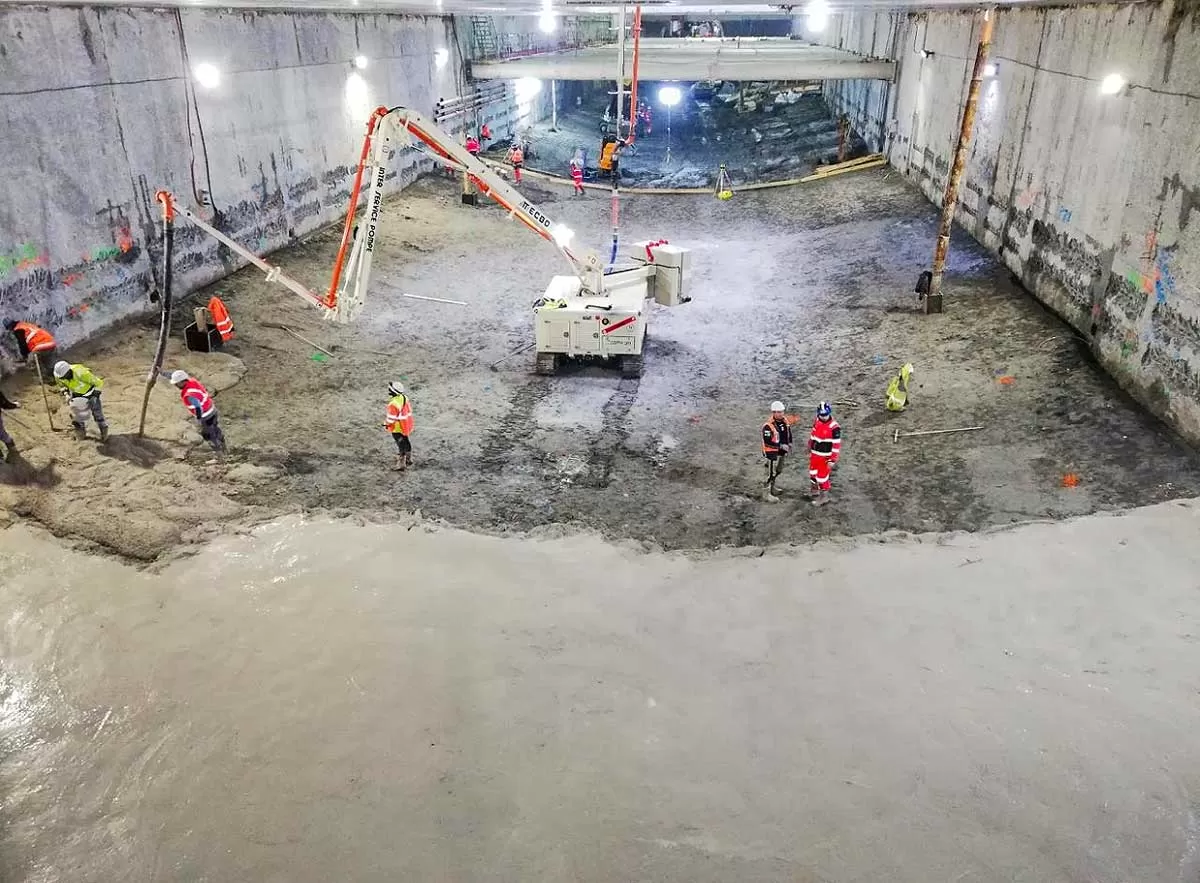

Mecbo America Launches Scorpion Concrete Crawler Boom
Mecbo America, a division of Blastcrete Equipment LLC, brings a new product to its lineup: the Scorpion Concrete Crawler Boom. The Scorpion provides contractors working in piling, drilling, tunnelling or commercial construction with a flexible arm for placing concrete where needed without disrupting the jobsite. It is an economical enhancement for contractors who have a concrete pump but need an effective way to deftly move material to spots that are difficult or unsafe to reach using other methods.“As concrete contractors grow and the scope of their work changes, many recognize the need for..
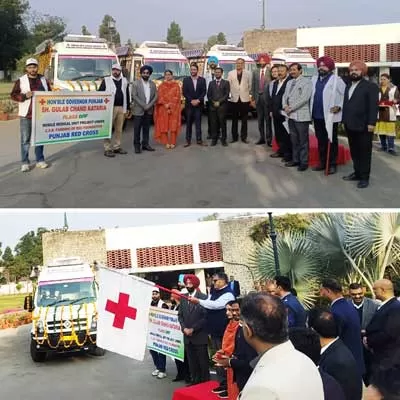

REC Flags off Mobile Medical Units Funded in Punjab
REC Limited, a Maharatna CPSE under the Ministry of Power and a leading NBFC, under its flagship CSR initiative Mobile Medical Units has committed Rs 42.9 million for the procurement and deployment of four Mobile Medical Units (MMUs) in 4 districts of Punjab. These units, handed over to the Indian Red Cross Society, Punjab, were flagged off by Hon’ble Governor Shri Gulab Chand Kataria Ji at Punjab Raj Bhawan.Serving as a lifeline for deprived communities, the MMUs will provide essential healthcare across four districts. REC Foundation continues to expand its CSR footprint, with various Mobil..